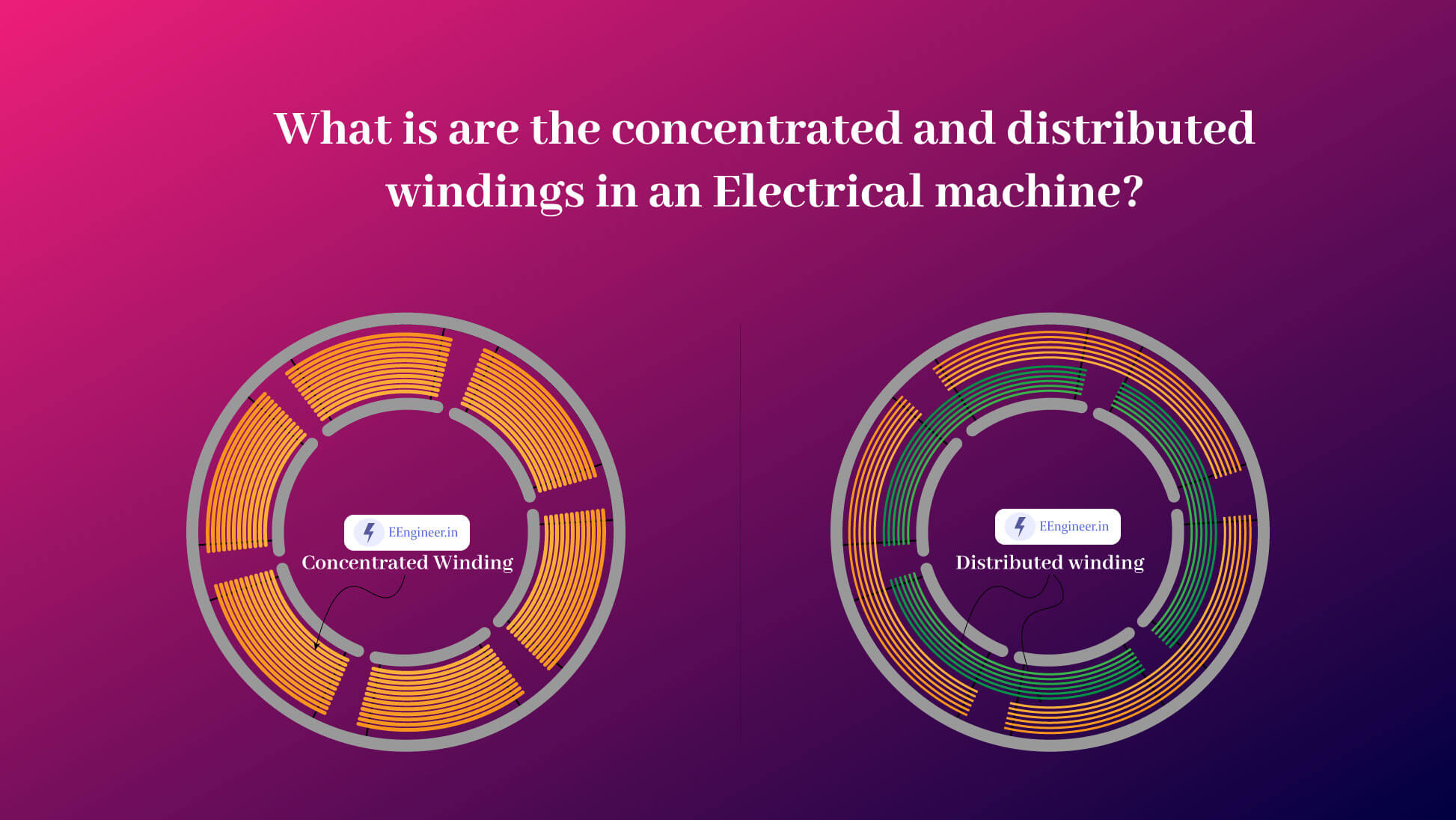
Electromagnetic armature winding creates magnetic poles, which can be concentrated as a single north and south pole in a concentrated winding configuration. However, in a distributed winding configuration, the armature has multiple north and south poles.
What you will know
Concentrated Winding:
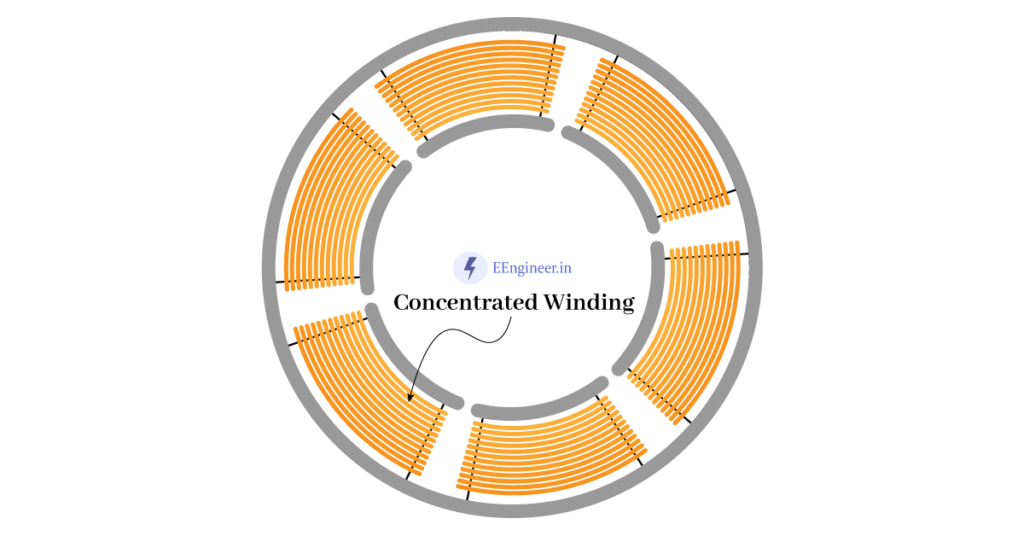
According to concentrated winding, the coil turns are concentrated in one place. So no production of the pitch factor or distribution factor for these winding. In addition, these windings have a unity Pitch factor and Distribution factor.
Firstly Consider a DC generator Machine.
- In Concentrated winding, the output voltage has more ripples than the Distributed winding.
- Hence, terminals of the distributed winding may deliver pure DC (Form factor: FF =1).
Below are some useful details related to concentrated winding:
| Coils | in series connection. |
| Number of poles | equal to the number of slots. |
| Coil type | Multi-turn coil. |
| Magnetic axis | Same for each turn of the single coil. |
| Application | Transformer winding, synchronous, and DC machine winding. |
Distributed winding
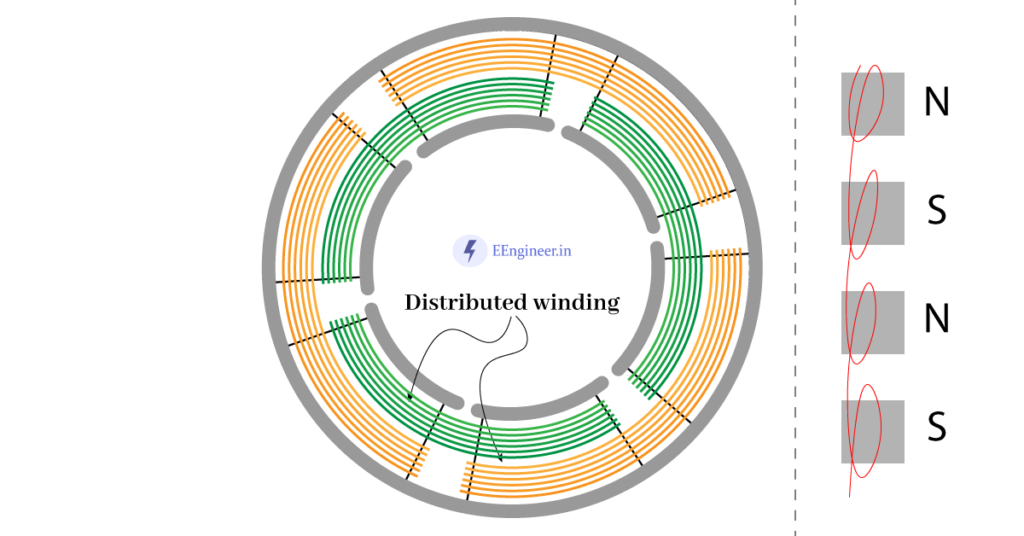
A winding that is spread throughout the periphery of the rotor/ stator having the least air gap is known as Distributed winding. In short, the EMF induced in it is due to the pitch factor or distribution factor. Further, It does not have the same magnetic axis for each coil. So this winding induces lesser EMF.
This winding is always better to use as it gives the best output waveform much closer to the sinusoidal waveform.
Below are some useful details related to Distributed winding:
| Coils | Along the air gap periphery. |
| Number of poles | Not equal to the number of slots. |
| Coil type | full pitched or distributed. |
| Application | Stator and rotor of the Induction Machine, the armature winding of synchronous. |
Check more articles related to the DC machine:
| Construction of DC machine | lenz’s law |
| faraday’s law | Active & Passive Elements |
Difference between Concentrated and Distributed winding
| Distributed winding | Concentrated winding |
| If coils of the winding of a single pole are distributed throughout the space is called Distributed winding. | If the Coils of the winding of a single pole are concentrated on one axis is called Concentrated winding. |
| A distributed winding is always wound on at least two stator teeth. | Whereas a concentrated winding is wound over only single stator teeth. |
| Practically, this type of winding is used in armature winding of the Induction machine, Synchronous machine, and DC machine. | But this type of winding is used in Transformers, Electromagnets, solenoids, etc. |
| Generally in Distributed winding number of poles is not equal to the number of slots. | But in Concentrated winding number of poles is equal to the number of slots |
Advantages of Distributed over the concentrated winding
There are several advantages of using distributed winding over concentrated winding in electrical machines:
- Reduced cogging torque: Cogging torque is the torque that is exerted on the rotor due to the interaction between the rotor and stator magnets. A distributed winding reduces cogging torque, leading to a smoother operation of the machine.
- Improved thermal performance: Distributed windings have better heat dissipation, which leads to a cooler operation of the machine and reduces the risk of thermal damage.
- Increased power density: Distributed windings allow for a higher power density, which means that more power can be generated from a smaller machine.
- Reduced ripple: Distributed windings reduce the ripple in the generated voltage, which leads to a cleaner output and improved efficiency.
- Improved reliability: Distributed windings are less prone to damage and have a longer life expectancy, which improves the reliability of the machine.
- Better mechanical stability: Distributed windings provide better mechanical stability, which helps to reduce the effect of mechanical vibrations on the machine.
lastly, Don’t forget to mention your thoughts on this in the comment box.
FAQs: Concentrated and distributed winding
What is the primary difference between distributed windings and concentrated windings?
Distributed windings have turns spread out over a significant portion, while concentrated windings have turns packed closely in a small section.
In terms of size, which type of winding is more suitable for smaller machines?
Concentrated windings are generally more suitable for smaller machines due to their space efficiency.
Are distributed windings more complex to manufacture than concentrated windings?
Yes, distributed windings are typically more complex to manufacture due to the spread-out arrangement of turns.
Which type of winding is known for better performance in terms of reducing harmonics?
Distributed windings are known for better performance in reducing harmonics compared to concentrated windings.
How do concentrated windings and distributed windings differ in terms of winding factor?
Concentrated windings have a lower winding factor, while distributed windings have a higher winding factor.
Which type of winding is commonly used in large machines like high-voltage transformers?
Distributed windings are commonly used in large machines like high-voltage transformers and generators.
Are concentrated windings more fault-tolerant compared to distributed windings?
Distributed windings are generally more fault-tolerant due to their spread-out arrangement.
Do concentrated windings or distributed windings have better cooling characteristics?
Distributed windings generally have better-cooling characteristics because of the larger surface area they cover.
Which type of winding is more cost-effective?
Concentrated windings are generally less expensive compared to distributed windings.
How do the two types of windings differ in terms of sensitivity to voltage imbalances?
Concentrated windings are more sensitive to voltage imbalances, whereas distributed windings are less sensitive.