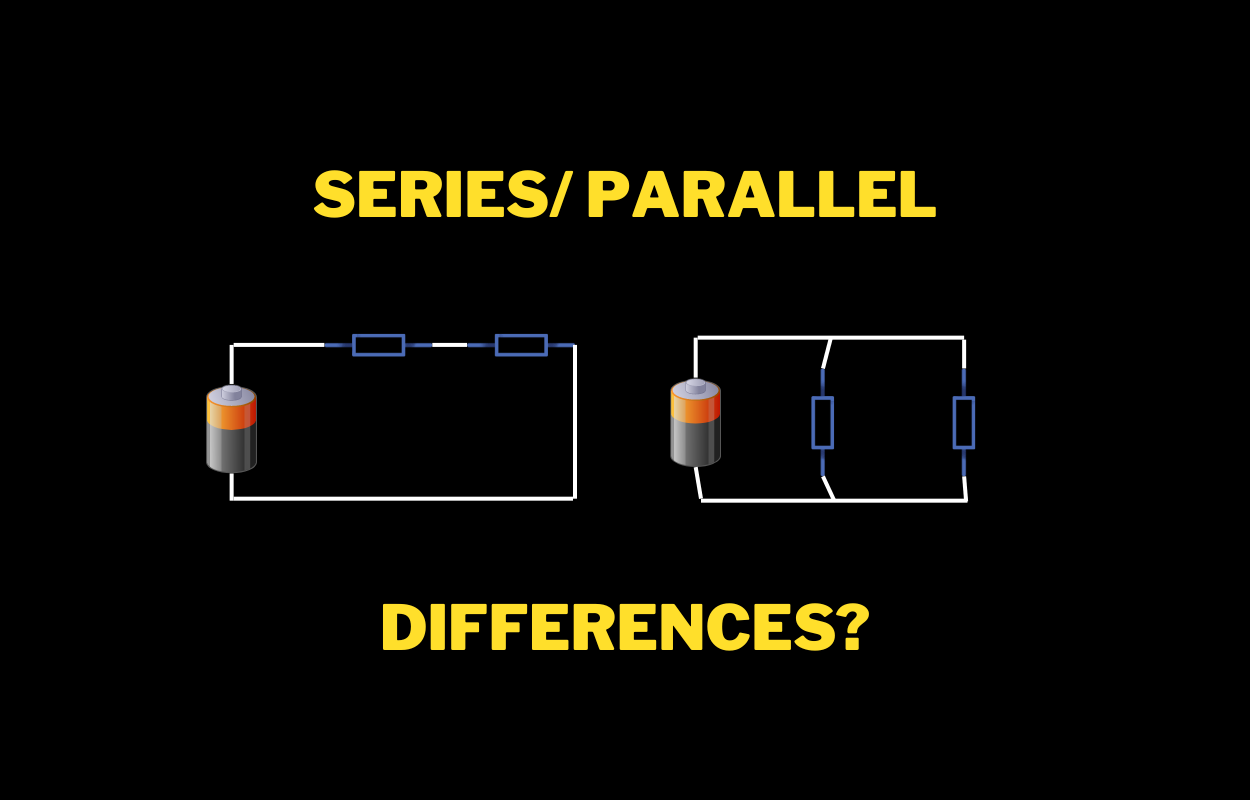
What is Active, Reactive and Apparent Power
In electrical engineering, understanding the types of power in an AC circuit is essential. The three key types of power are Active Power, Reactive Power, and Apparent Power. These terms help explain how energy is consumed, stored, and transferred in electrical systems. ⚡ What is Active Power? (True or Real Power) Definition:Active Power (also known … Read more